Artificial intelligence did not come out of nowhere. Although the term gained popularity in 1955, after John McCarthy’s workshop at Dartmouth College, its history traces back thousands of years.
Before going further into the understanding and functions of AI, it would be beneficial to familiarize yourself with the two most common terminologies: Machine learning (ML) & Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Machine learning involves a technique that trains and teaches machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time.
Artificial intelligence aims to create machines capable of performing tasks, typically requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, learning and decision-making.
To generalize, AI refers to applications that can perform complex tasks that once required humans to complete. AI developers have dedicated years to crafting tools that enhance productivity, efficiency, and intelligence across various industries. The goal is to mimic and improve how humans perceive and interact with the world. This process of automation can bring incredible value to your business.
Over the past few years, AI tools spread widely, making them available to the public. Now anyone with access to the internet can use these tools.
We can see businesses worldwide gradually integrating them into their day-to-day and encouraging their workforce to adapt to the reality that AI is here to stay. While concerns exist about AI replacing jobs, employers emphasize that the primary purpose of these tools is to augment performance and streamline tasks, not to replace human input.
Even though the adoption and use of these publicly available tools gained quick popularity, the Arab world seems to be falling behind.
Where the Arab world stands on AI
Interest in AI has been increasing in the region for some time, mostly within government entities.
Saudi Arabia ranks second globally in AI awareness based on Stanford University’s USA’s Artificial Intelligence Index Report, with China topping the list.
The ranking shows the Saudi population’s positive reception of AI tools, services and general optimism towards transformative technology.
While government offices are actively pushing narratives surrounding AI, the younger generation doesn’t seem to have embraced popular tools and injected them into their daily use. There are several factors at play here, the main one being the complexity of the Arabic language with all its dialects and the lack of enough content and information available to train AI tools using machine learning.
The most significant steps taken by governments in the region come from the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
In 2018, the UAE formed the Council for Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain, tasked with proposing policies for an AI-friendly ecosystem, advancing research and promoting collaboration between private and public sectors.
In 2019, Saudi Arabia established the Saudi Data & AI Authority (SDAIA) to create a national strategy to help achieve Saudi Vision 2030.
Both entities have so far achieved in facilitating funding and education opportunities in the field of Artificial Intelligence. There are more similar initiatives out there.
However, the main challenge remains in collecting enough data from Arabic speakers to improve at a similar pace as other parts of the world. This is where media monitoring comes into play to bridge the gap.
AI in the media monitoring industry
Before the adoption of AI tools, media monitoring was tedious and time-consuming. It involved manually collecting and processing data from various media sources like news articles, social media, blogs and websites. Companies relied on humans to gather, categorize and then analyze all this data, which lacked accuracy and efficiency, to make them reliable and actionable for organizations.
By eliminating these primary challenges, AI made these autonomous tasks faster, more accurate and opened up new possibilities for the industry. Because of the vast amount of data at its disposal, AI makes it easy to identify patterns, understand sentiments, monitor in real-time and produce insights, among other things.
With this in mind, it is now easier and less time-consuming to read data and use it as actionable insights. All these advancements pushed the media monitoring industry to new heights, increasing the demand and value of their services.
Now companies act, react and engage more efficiently, thanks to media monitoring platforms. AI didn’t only provide automation and efficiency, it introduced the ability to monitor in real-time and generate insights to make informed decisions. Consider how important this can be when you launch a critical campaign, detect a potential crisis before it escalates and identify emerging trends before your competitors.
Sensika’s goal is to bring all these capabilities to Arabic-speaking countries.
Sensika’s AI tools
The key to making AI tools more potent is rigorous training.
Sensika has been active in the MENA region for the past 7 years, which allowed us to arm our platform and analysts with unparalleled accuracy and understanding of the Arabic media landscape.
Because of our commitment to delivering tailored solutions to Arab-speaking organizations and our years of experience, we earned the trust of esteemed clients across MENA.
Let us take a look at some of the remarkable AI tools that Sensika uses as part of its cutting-edge media monitoring platform:
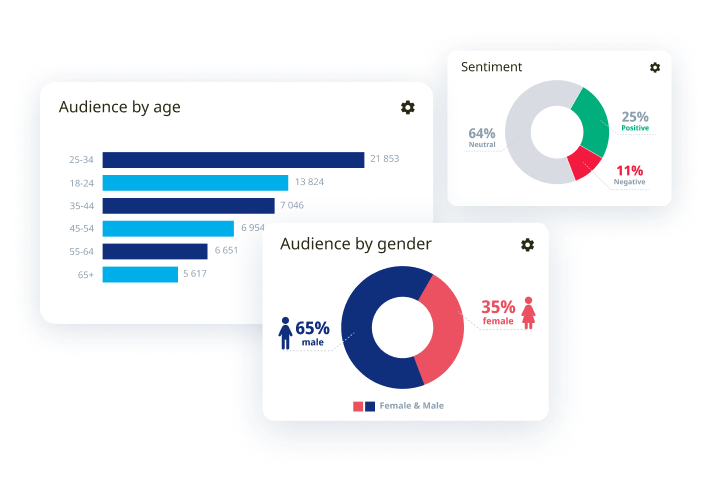
Sentiment Analysis:
Our Sentiment Analysis tool offers real-time monitoring of how the public perceives specific topics, brands, or events. By interpreting emotions and attitudes expressed in the media, this sophisticated analysis categorizes sentiment into three categories: positive, negative, and neutral. It gives valuable insights into public opinion, helping you gauge the sentiment surrounding your interests.
Named Entity Extraction:
Our Named Entity Extraction tool identifies crucial information within texts, such as names of people, organizations, places, and products. Organizing content into categories facilitates a better understanding of the context and allows you to focus on specific entities. This tool streamlines information retrieval, providing a clearer picture of the discussed subjects.
Entity Disambiguation:
Leveraging Wikidata’s open-source database, our Entity Disambiguation ensures accurate comprehension of mentions in various languages or forms. This process guarantees precise results and a deeper understanding of the text, even when referring to the same thing or person differently.
Topic Classification:
Organizing your content into topics enhances the precision of your analysis. Our Topic Classification tool offers filtering options, enabling easy access to specific topics within the monitored data. It streamlines content exploration, empowering you to find the information most relevant to your interests.
Keyword Extraction:
Our Keyword Extraction tool automatically detects the most relevant keywords and phrases in your data, providing an instant overview of the main themes and topics. By leveraging the most frequently used keywords, you can optimize your messaging for better engagement.
Related content detection and grouping:
Our AI model identifies related content in several languages, grouping them. This functionality assists media professionals in understanding the broader context of their monitoring efforts, offering comprehensive insights.
Machine translation:
We integrate Google Translate into our feed to automatically translate content to your preferred language. This feature ensures you can understand and analyze content from different regions efficiently.
Abstractive summarization:
Powered by the ChatGPT model, our Feed offers concise synopses or summaries of original content. This abstractive summarization helps you quickly grasp the main points of articles, improving content comprehension.
Face recognition:
Our automatic face recognition feature trains the algorithm to detect key individuals in images and videos of interest, enhancing your media monitoring capabilities.
Speech-to-text processing:
Our feed can transcribe audio and video content, making it searchable and accessible for further analysis.
AI-enhanced Search:
Our AI-enhanced Search feature allows real-time searching and filtering of indexed media content using keywords or advanced logic. Filter criteria based on structured data extracted from unstructured data further refine the search results.
Keyword Suggestions:
Our AI-assisted search functionality simplifies query building by suggesting relevant keywords and word forms in many languages. Morphological expansion enhances the efficiency of querying and filtering indexed content.
AI-enhanced Source Analysis:
With this feature, we make it easy to identify unauthenticated influence networks and misinformation campaigns. Our ML model analyzes the entire source catalogue, revealing trends, patterns, and relationships within the media landscape.
Conclusion
Arab nations thrive to be world leaders in technological advancements. With upcoming smart city projects and digitalized platforms for citizens, new challenges will present themselves.
Sensika aims to bring advanced capabilities to the Arab world, supporting the region’s vision for the future.
If you want to learn more about how Sensika’s media monitoring platform can benefit your business, browse our website for specific use cases, customer stories and more or book a demo with us.



